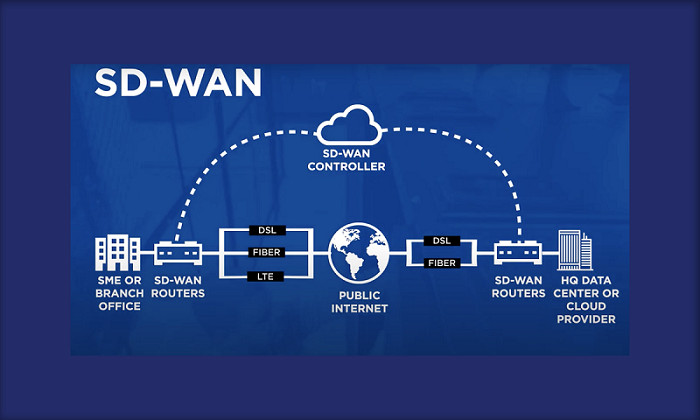
The Software-Defined Wide Area Network market is expanding as enterprises replace rigid MPLS-only architectures with application-aware connectivity. SD-WAN combines centralized control with dynamic path selection, letting organizations use multiple links—broadband, LTE/5G, and MPLS—while optimizing performance for critical applications. This matters as business traffic shifts to cloud and SaaS, where backhauling through data centers adds latency and cost. SD-WAN improves user experience by steering traffic based on loss, latency, and jitter, and by prioritizing real-time apps like voice and video. It also simplifies branch deployments with zero-touch provisioning and centralized policy management. Organizations adopt SD-WAN to reduce WAN spend, increase resilience, and accelerate site rollouts. It is especially valuable for distributed enterprises, retail chains, healthcare networks, and hybrid work environments needing consistent performance and visibility across many locations.
Architecture typically includes edge devices or software clients at sites, plus centralized controllers and orchestrators. Policies define how applications are identified and routed, and how traffic is secured. Many solutions support segmentation to isolate business units or sensitive workloads. Integration with cloud on-ramps improves access to major SaaS and IaaS providers. Visibility is a core benefit: SD-WAN analytics show application usage, link quality, and performance trends, enabling proactive troubleshooting. However, SD-WAN success depends on correct design—link sizing, redundancy planning, and policy tuning. If broadband quality is inconsistent, organizations may need multiple providers or wireless backup. Some deployments also combine SD-WAN with optimization features like forward error correction and packet duplication for real-time traffic. As networks become more software-driven, ongoing monitoring and governance become essential. Teams must manage firmware updates, security policies, and configuration changes across large fleets without disrupting business operations or user experience.
Security has become inseparable from SD-WAN decisions. Branches need secure internet breakout, encryption, and consistent policy enforcement. Many vendors bundle next-generation firewall features, secure web gateways, or integrate with SASE frameworks that deliver security services from the cloud. Zero trust principles influence design, including identity-based access and segmentation between users, devices, and applications. Organizations also require centralized logging and integration with SIEM tools for incident detection. Regulatory requirements can drive the need for strong audit trails and policy consistency across regions. Vendor choice increasingly depends on how well SD-WAN integrates with security stacks and cloud environments. Operationally, organizations must decide whether to manage SD-WAN in-house or use managed services. Managed SD-WAN can reduce staffing burden and accelerate rollout, but buyers must assess SLAs, support responsiveness, and change control procedures carefully to avoid loss of agility and visibility.
The future of SD-WAN will align closely with SASE and cloud networking. More policies will be identity- and application-centric, and more traffic will be secured and optimized through cloud points of presence. AI-driven analytics will help detect anomalies, predict link degradation, and recommend policy adjustments. 5G will increasingly serve as primary or backup connectivity for branches and temporary sites, increasing the need for intelligent link management. As enterprises consolidate networking and security vendors, integrated SD-WAN/SASE solutions may gain traction, though interoperability remains important. Organizations evaluating SD-WAN should focus on measurable outcomes: improved application performance, reduced outages, faster site deployment, and simplified operations. A phased rollout—piloting a few sites, validating policies, then scaling—reduces risk. With thoughtful design and governance, SD-WAN becomes a core foundation for cloud-first enterprise networking and resilient distributed operations.
Top Trending Reports: